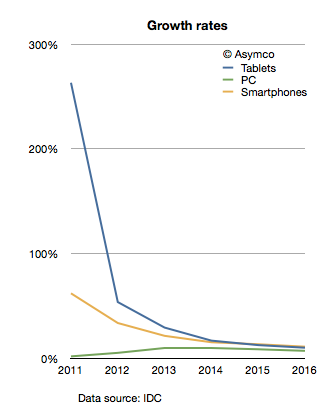
“Within five years after discount retailing pioneer Korvette’s opened its first store in 1957, over a dozen copycat discounters had emerged. In contrast, the giant discount furniture retailer IKEA has never been copied. The company has been slowly rolling its stores out across the world for [close to 50] years; and yet nobody has copied IKEA.
Why would this be? It’s not trade secrets or patents. Any competitor can walk through its stores, reverse engineer its products and copy its catalog. It can’t be that there is no money to be made: its owner Ingvar Kamprad is the third richest person in the world. And yet nobody has copied IKEA.
Our sense is that the other furniture retailers have followed the positioning paradigm and defined their business in terms of product and customer categories, which are readily copied. Levitz Furniture, for example, sells low-cost furniture to low income people. Ethan Allen sells colonial furniture to wealthy people.
IKEA, in contrast, has organized its business around a job to be done: “I need to furnish my apartment (or this room) today.” When this realization occurs to people anywhere in the developed world, the word IKEA pops into their minds. IKEA is organized and integrated in a completely different way than any other furniture retailer in order to do this job as well as possible.”
Integrating Around the Job to Be Done (Clayton Christensen, Harvard Business School; Scott Anthony, Innosight LLC, Scott Cook, Intuit; Taddy Hall, Advertising Research Council).
IKEA is the world’s leading furnishing retailer and an amazing success story. As Christensen points out the success is all the more perplexing because it seems perfectly defensible. Nobody has tried to duplicate or undermine IKEA.
Positioned around a clear job-to-be-done it integrated design, manufacturing and distribution (including warehousing) as well as “big box” retailing as an experience.
This may sound familiar.
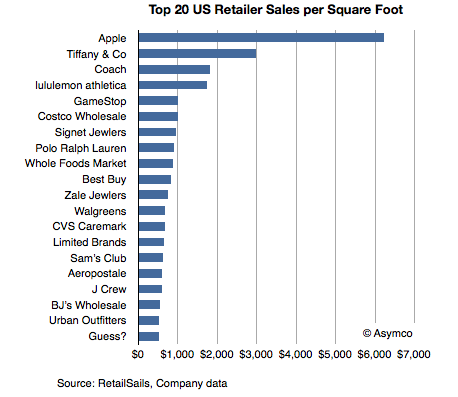
Apple’s entry into retail depended on a clear job-to-be-done, design, carefully selected merchandise and retailing as an experience. Similar to IKEA, Apple also became a dominant player in its segment and even achieved seventeen times better performance than the average US retailer in terms of sales per square foot.
At first glance they seem to be similar businesses in terms of strategy or “architecture” but how do the actual businesses stack up? Can we find data to support any claim of similarity. Continue reading “What retail is hired to do: Apple vs. IKEA”