Continuing from Will Apple rule the iPad market? | Asymco.
The first claim is that
it is unclear if [Apple] will end up dominating the market the way it has come to rule the digital music player market with the iPod.
After hearing a thousand voices cry out that the iPad is nothing more than a bigger iPod touch (which, plainly, it is) it’s amusing to read that its similarity with a sibling ends when it comes to market performance.
Let me make one claim up-front: the iPad is more of an iPod than the iPod.
The original iPod was successful because it had a significant integrated value chain bolted on. Apple disrupted music with a value chain, not a product. It changed the way music is bought, consumed and even how it is produced. It changed the economics from retail down to songwriting.
This is why it came to dominate its market. Every competitor that took a run at it did so with a partial solution to the value chain. Often it was nothing more than a music player, and in some cases (e.g. Zune) it was bundled with some other pieces of technology, but poorly executed and too late.
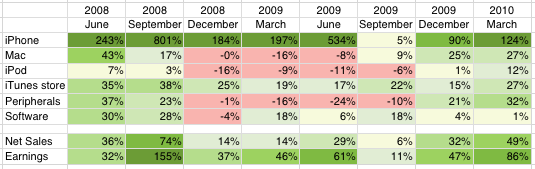
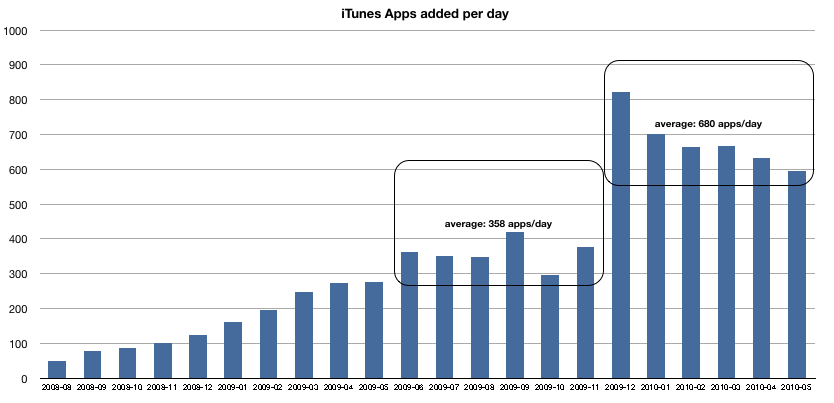
The iPad comes with an even bigger value chain bolted on: the App Store. Apple is flogging not just an “app player” but also a new way to develop and distribute software. If you cut “music” and paste “apps” you see the immediate parallel between iPod and iPad. The app ecosystem will quickly grow to be larger than the music ecosystem with the mobile software business already eclipsing the music business.
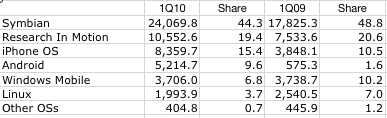
A competitor launching a tablet device will have to somehow overcome the momentum of billions of downloads fed by hundreds of thousands of apps built by tens of thousands of developers for hundreds of millions of users.
The iPod juggernaut pales in comparison to the iPad supernova. The iPod had no apps or dedicated developers. Its ecosystem consisted of a handful of music companies. The only thing that made it “sticky” was the tie-in with one type of content.
The iPad on the other hand has a thousand other jobs to do for its users. It has a rich tapestry of functionality and a multi-dimensional (literally) user experience. It’s a platform. It’s even powerful enough to impose new standards on the web itself and to suggest that search is a bygone activity.
So to suggest that Asus or Dell will somehow build “iPad killers” sounds asinine. These competitors don’t even grasp what the product is and what it’s for. Sony said they don’t see a market for it. Microsoft, trapped in the innovator’s dilemma and overshooting the market by miles, said they don’t understand what the point is because users want full PCs. Google asked what’s the value of a big iPod. I could go on, but there was not a single company in the industry who recognized what they were looking at in January. Apple keeps a tight lid on new products so that competitors don’t get a head-start on copying, but in the case of the iPad, advance knowledge would not have had any impact. Competitors look at the iPad and see nothing. They’ll only react once the market explodes and they start to feel belated pain.
If, and it’s a big if, they do recognize what an iPad is, their response cycle is going to be measured in years. On hardware, they were blown away with a product that had twice the power, half the bulk, twice the battery life with half the price of what they had on the shelf. They may catch up on hardware in a year or two and launch some sort of iPad-like assembly of components, but that is like making the first iPod killer in 2002.
Then there is software. Their software supplier (Microsoft of Google) will have to build a platform that works. That will take years. Years during which the iPad will penetrate every geography, demographic and vertical market.
Google might move more rapidly than Microsoft, but they will produce an open source poster child of a platform. Fragmented and rough around the edges to the point of looking like a hobby project. Their flea market store will also have the smell of fresh glue about it. Microsoft is so far behind the curve that I don’t even think they will try to move the tiller. Their view of the market was betrayed by the recently knifed Courier demoware. To suggest a challenge to the PC/Windows model inside Microsoft is a career-limiting move so don’t expect their brightest to be lining up to propose new platforms to management.
What about HP? Assuming they overcome the pitfall of NIH that kills 80% of integration efforts, they will still need to perform an enormous amount of heavy lifting to get WebOS to be a competitive experience on a tablet. Most opinions were that Palm came pretty close with a smartphone, but that was nowhere near enough to stay alive, never mind challenge iPhone.
Then there is the ecosystem. Building it is just not something I can even begin to roadmap. What about developer tools, SDKs, frameworks and evangelism? With a Palm division, HP is the best positioned of the PC vendors but it has a chance at being a player as much as Creative did vs. the iPod, or needless to say, Palm vs. the iPhone.
So the iPad challengers face five daunting obstacles:
- Recognition of a threat from a seemingly benign product
- Execution on hardware against the best integrator on the planet
- Execution on software against a new UI metaphor fortress surrounded by a patent moat
- Integration of hardware and software to a sublime whole
- Re-building a value chain for which they have no handle vs. a broad and deep existing universe of app/content creation distribution and consumption enjoying logarithmic network effect value.
That does not even touch the logistics, sourcing, margin and pricing challenges of world-wide distribution of the whole value chain. Nor does it cover the lock-in of advertisers to new tools for creatives or the billions of daily views from a platform that is blindingly dazzling.
To put it in the language of disruption, by the time the competitors launch symmetric attacks on the iPad, Apple will be the incumbent. And we all know that symmetric attacks never work against entrenched incumbents who have all the levers of power at hand to deploy in a withering counter-attack.